New Publication - Multi-scale seismic reliability assessment of networks by centrality-based selective recursive decomposition algorithm
A journal paper, titled “Multi-scale seismic reliability assessment of networks by centrality-based selective recursive decomposition algorithm” (Lee & Song*, 2021), was recently published in Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics. The paper was co-authored by me and Prof. Junho Song (Seoul National University).
The permanent link via DOI number of the paper is HERE. The full reference information is as follows.
Lee, D., & Song, J. (2021). Multi-scale seismic reliability assessment of networks by centrality-based selective recursive decomposition algorithm. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics. Vol. 50(8), 2174-2194.
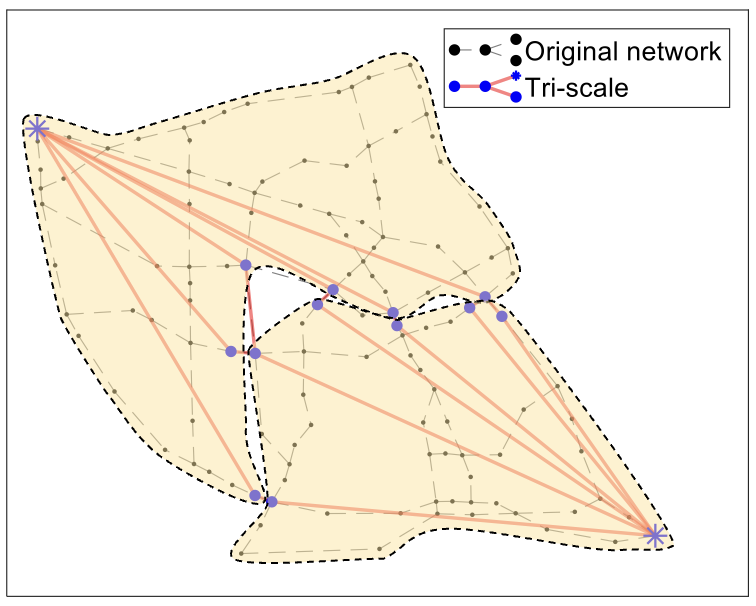
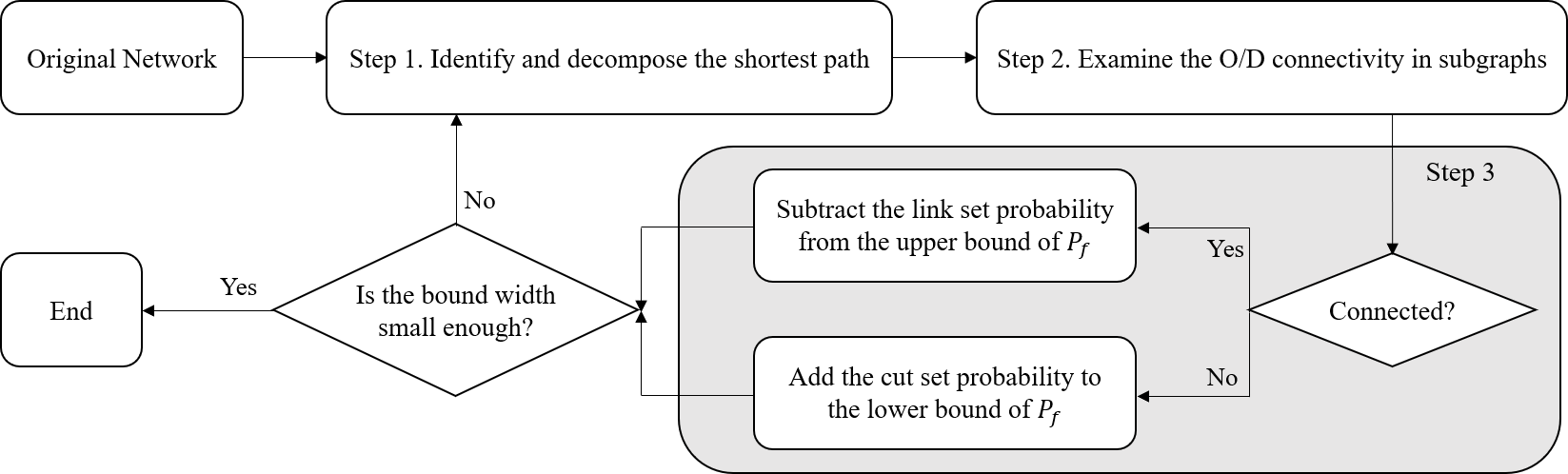
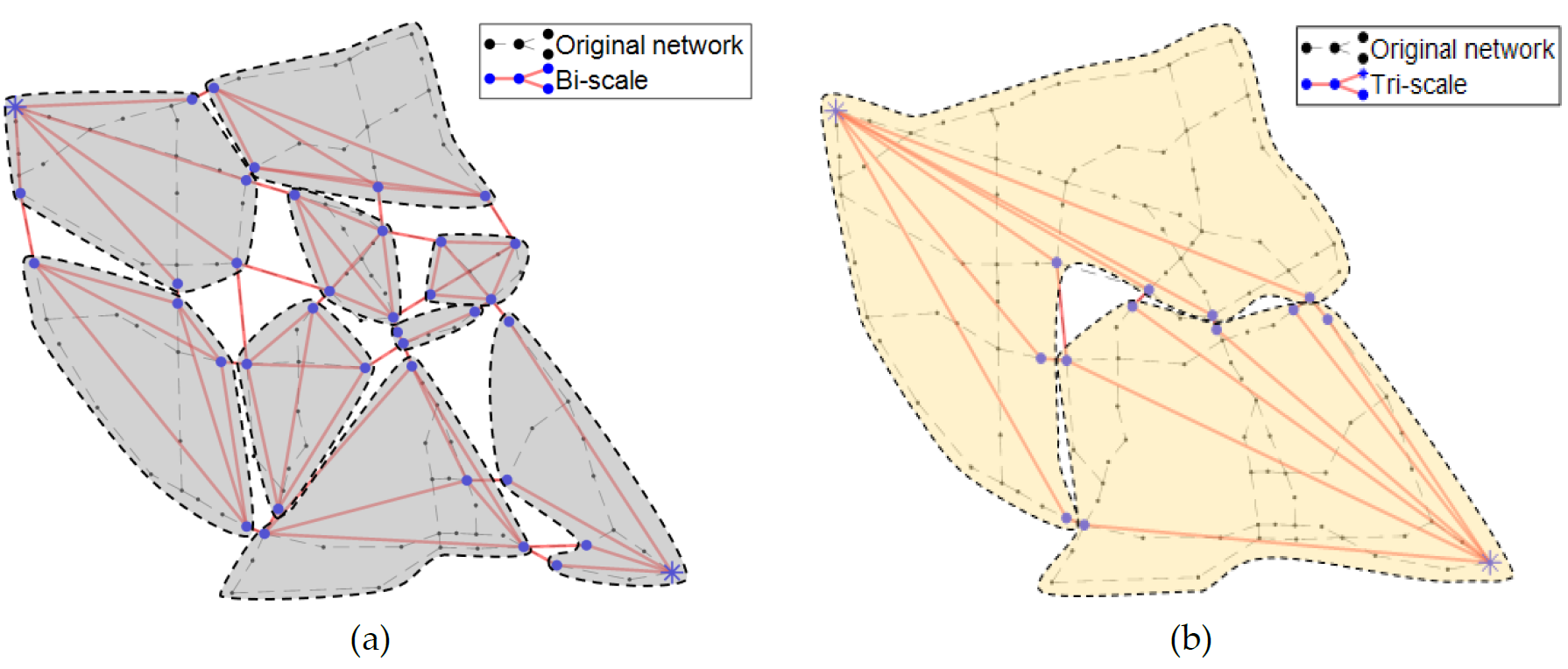
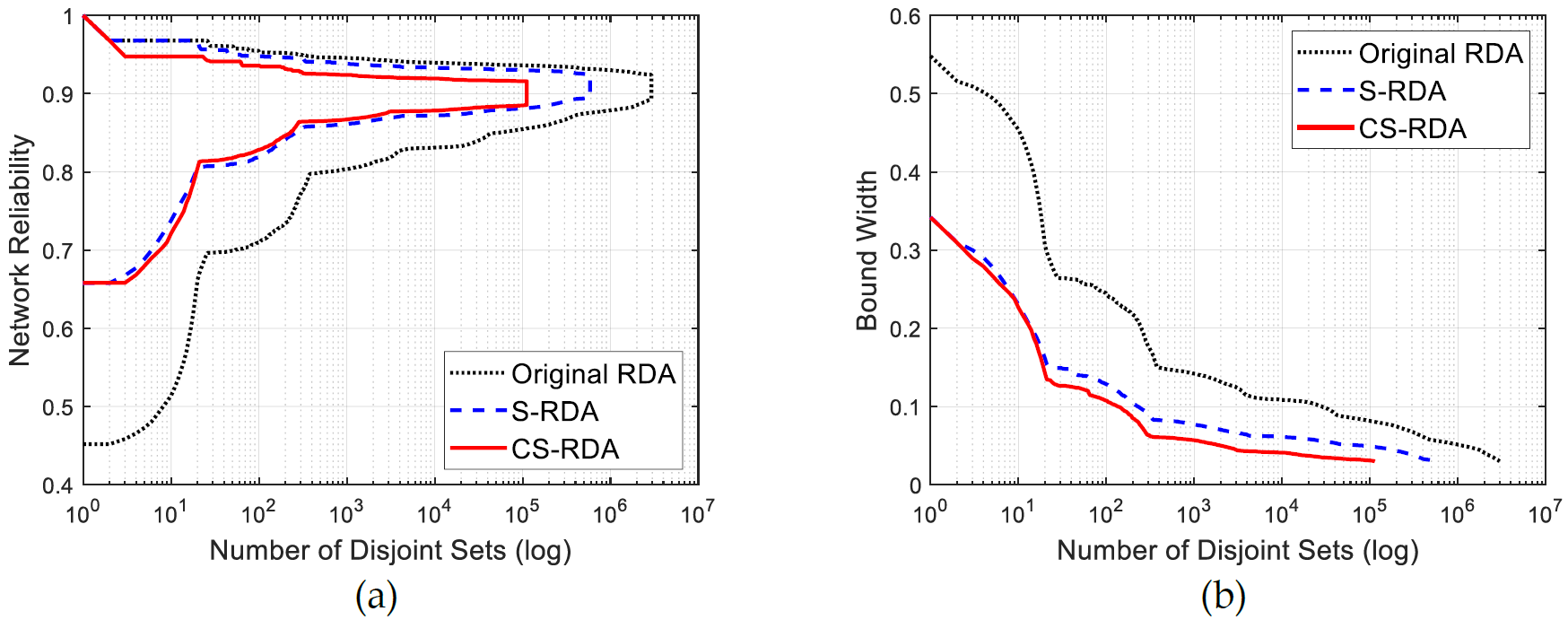
This paper proposed a new non-simulation-based algorithm to analyze the post-hazard network connectivity promptly but accurately. To this end, two algorithms were developed and utilized: (1) centrality-based selective recursive decomposition algorithm (CS-RDA), and (2) edge-betweenness algorithm. First, CS-RDA finds the most reliable path between an origin and destination (O/D) node pair, and decompose the network into subgraphs by removing the nodes in the path in order of network centrality. The O/D connectivity and its probability in subgraphs are recursively assessed until the width of bounds on the O/D connectivity converge to a certain level. In addition, a multi-scale analysis utilizing edge-betweenness algorithm enables CS-RDA to overcome the computational limitation in large-scale networks without compromising accuracy. The numerical examples including a hypothetical network and highway bridge networks in San Jose and San Diego demonstrate the performance and merits of the proposed methods.
Abstract
As lifeline networks such as transportation or electricity networks in modern societies are intricately interlocked, a small number of components damaged by natural or man-made disasters can have a great impact on network performance. For this reason, it is essential to assure the capability of rapid assessment of network reliability to make prompt follow-up measures. Despite the rapid development of various algorithms and computing power, the capability is still limited due to computational cost for analyzing the connectivity of a single origin and destination (O/D) node pair in large-scale networks. Therefore, this paper introduces a new algorithm utilizing network centrality, termed “centrality-based selective recursive decomposition algorithm” (CS-RDA). By preferentially decomposing the node which is most likely to belong to the min-cut identified based on the betweenness centrality, the convergence of the bounds on the O/D connectivity can be expedited significantly. This paper also introduces a new multi-scale analysis approach termed “edge-betweenness algorithm.” The algorithm groups components such that its modularity is maximized, by sequentially removing edges that have the highest level of betweenness centrality. As a result, the reliability of large-scale networks can be accurately evaluated in a short time owing to the reduced complexity of the simplified network. The proposed methods are successfully demonstrated by a hypothetical network example, the highway bridge networks in San Jose and San Diego in California, USA.
Acknowledgment
- This work is supported by a grant from Smart Civil Infrastructure Research Program funded by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (21SCIP-B146946-04).
References
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: