New Publication - Risk-informed operation and maintenance of complex lifeline systems using parallelized multi-agent deep Q-network
A journal paper, titled “Risk-informed operation and maintenance of complex lifeline systems using parallelized multi-agent deep Q-network” (Lee & Song*, 2023), was recently published in Reliability Engineering & System Safety. The paper was co-authored by me and Prof. Junho Song (Seoul National University).
Through the support by Seoul National University, the paper was published as an Open Access article, and thus downloadable for free. The permanent link via DOI number of the paper is HERE. The full reference information is as follows.
Lee, D., & Song, J. (2023). Risk-informed operation and maintenance of complex lifeline systems using parallelized multi-agent deep Q-network. Reliability Engineering & System Safety. Vol. 239, 109512.
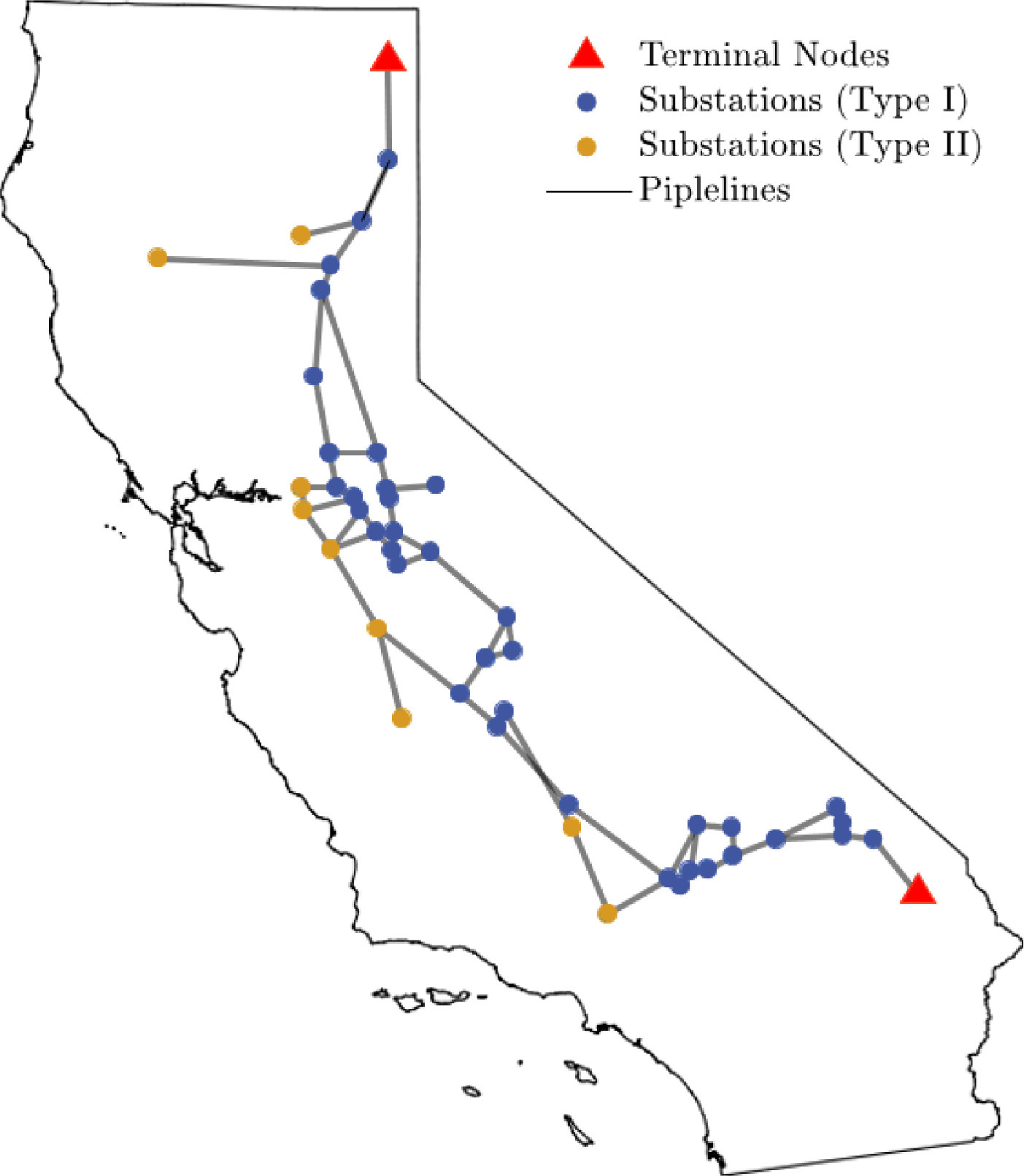
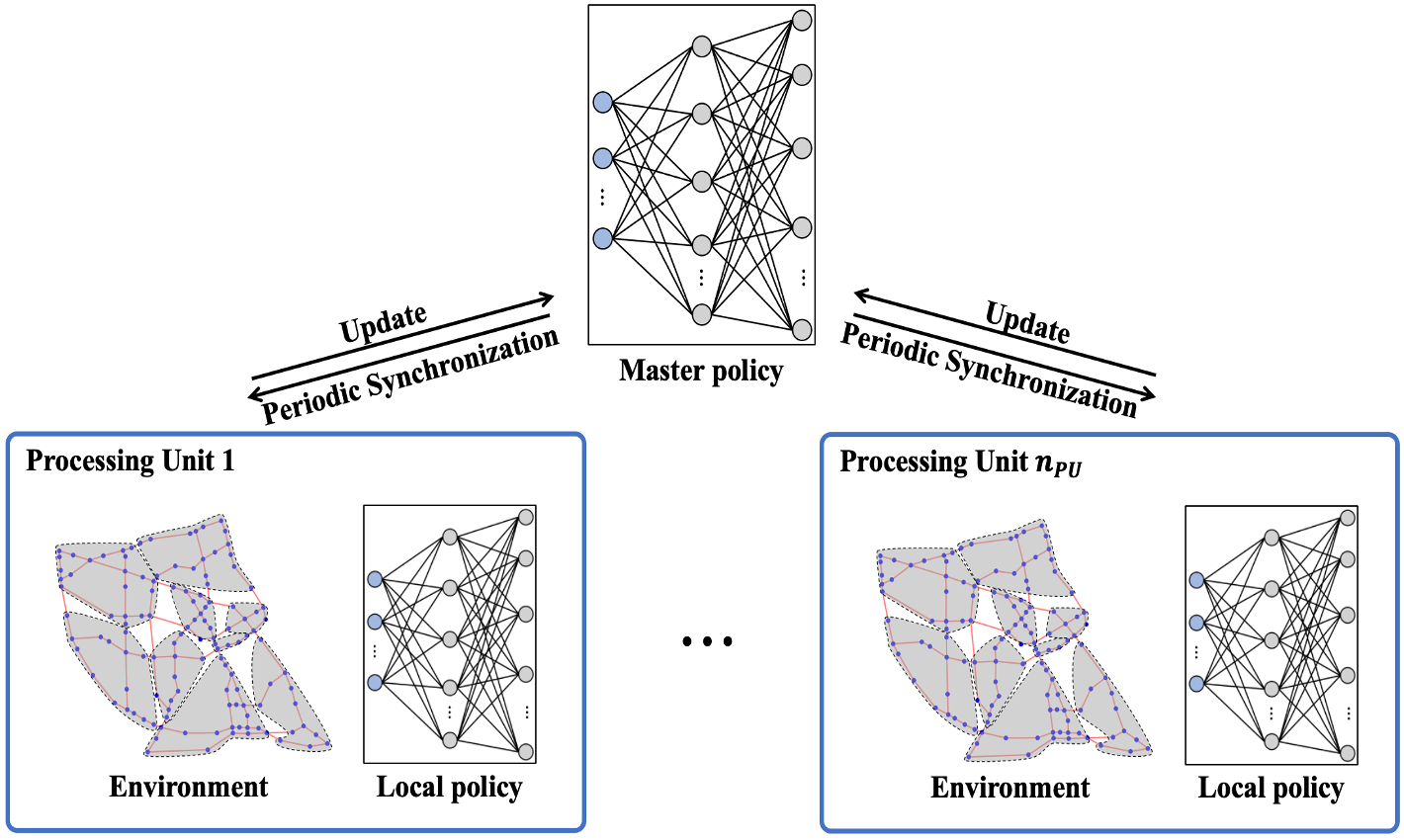
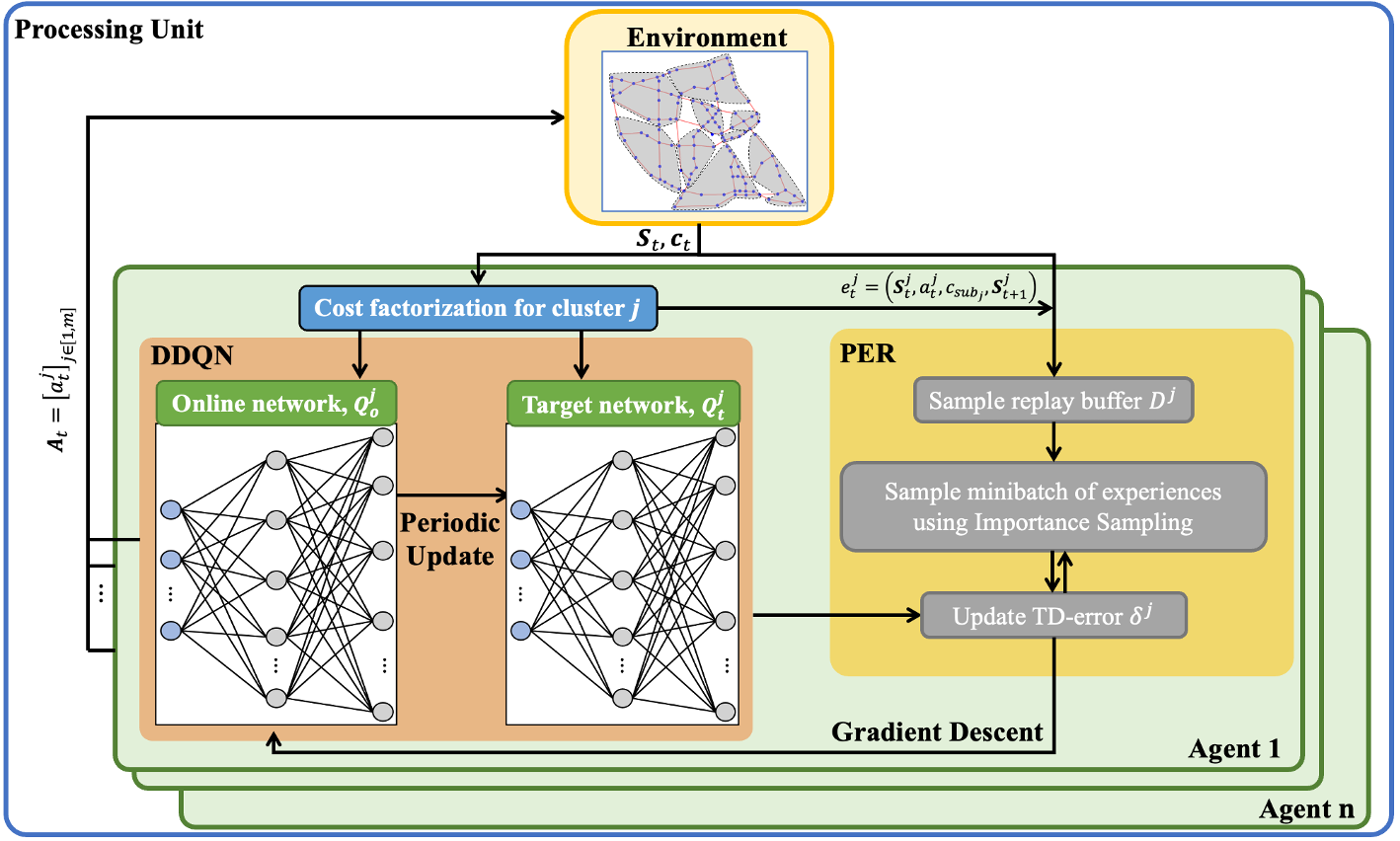
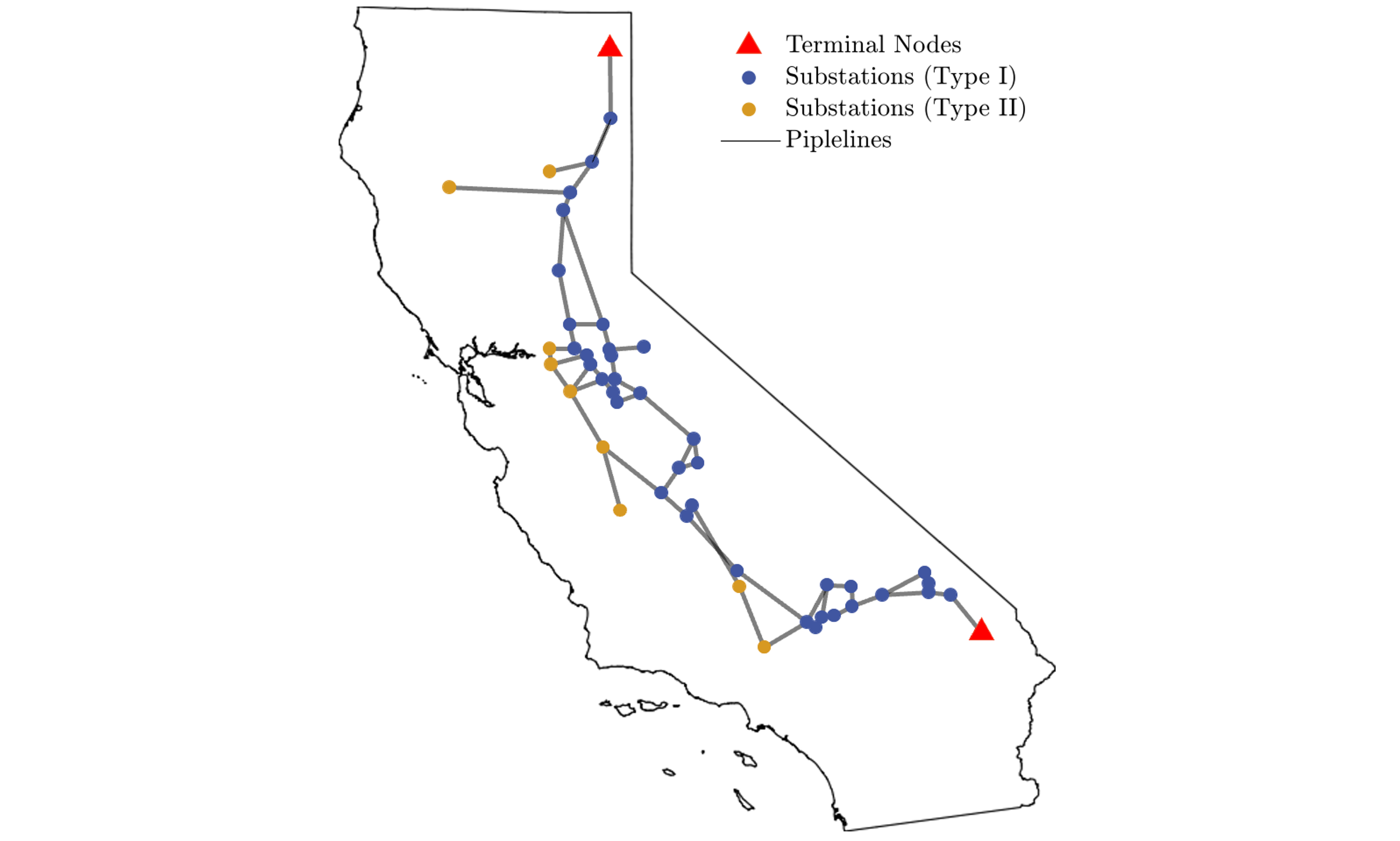
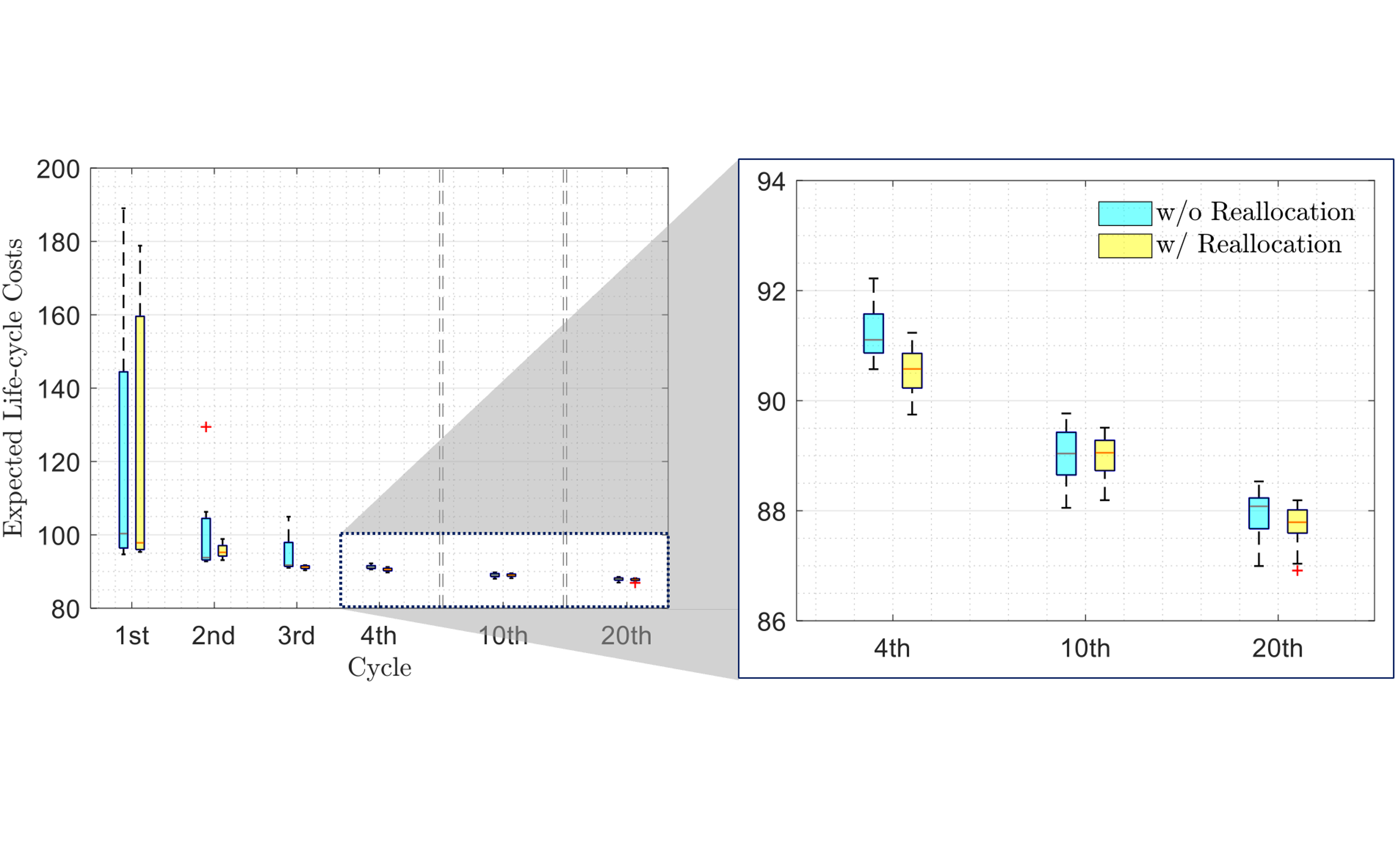
This paper proposes a multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) framework, called parallelized multi-agent deep Q-network (PM-DQN), for efficient risk-informed operation and management (O&M) of lifeline systems. PM-DQN introduces a divide-and-conquer strategy with community detection to explore the optimal policy with low computational cost. The strength of the proposed algorithm is further enhanced by hyperparameter tuning and periodic synchronization combined with parallel processing. The applications to the multi-state general system and the realistic gas distribution system successfully demonstrate the performance and advantages of the proposed method. In both examples, the proposed method outperforms conventional O&M methods and other MARL-based methods in terms of computational time and expected life-cycle cost. Furthermore, the second example demonstrates that the proposed framework of agent deployment and periodic synchronization of multiple processors can be applied to other DRL methods.
Abstract
Lifeline systems such as transportation and water distribution networks may deteriorate with age, raising the risk of system failure or degradation. Thus, system-level sequential decision-making is essential to address the problem cost-effectively while minimizing the potential loss. Researchers have proposed to assess the risk of lifeline systems using Markov decision processes (MDPs) to identify a risk-informed operation and maintenance (O&M) policy. In complex systems with many components, however, it is potentially intractable to find MDP solutions because the numbers of states and action spaces increase exponentially. This paper proposes a multi-agent deep reinforcement learning framework, termed parallelized multi-agent deep Q-network (PM-DQN), to overcome the curse of dimensionality. The proposed method takes a divide-and-conquer strategy, in which multiple subsystems are identified by community detection, and each agent learns to achieve the O&M policy of the corresponding subsystem. The agents establish policies to minimize the decentralized cost of the cluster unit, including the factorized cost. Such learning processes occur simultaneously in several parallel units, and the trained policies are periodically synchronized with the best ones, thereby improving the master policy. Numerical examples demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms baseline policies, including conventional maintenance schemes and the subsystem-level optimal policy.
Acknowledgment
- This first author is supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. RS-2022-00144434). The corresponding author is supported by the Institute of Construction and Environmental Engineering at Seoul National University.
References
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: