New Publication - Dual graph-based Bayesian network modeling with Rao-Blackwellization for seismic reliability and complexity quantification of network connectivity
A journal paper, titled “Dual graph-based Bayesian network modeling with Rao-Blackwellization for seismic reliability and complexity quantification of network connectivity” (Lee et al., 2025), was recently published in Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics. The paper was co-authored by me, Prof. Ji-Eun Byun (University of Glasgow), and Prof. Junho Song (Seoul National University).
Through the support by Seoul National University, the paper was published as an Open Access article, and thus downloadable for free. The permanent link via DOI number of the paper is HERE. The full reference information is as follows.
Lee, D., Byun, J.E., & Song, J. (2025). Dual graph-based Bayesian network modeling with Rao-Blackwellization for seismic reliability and complexity quantification of network connectivity. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics. Vol. 54(10), 2387-2402.
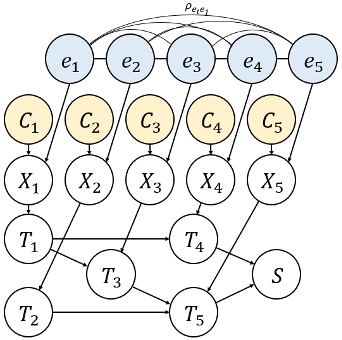
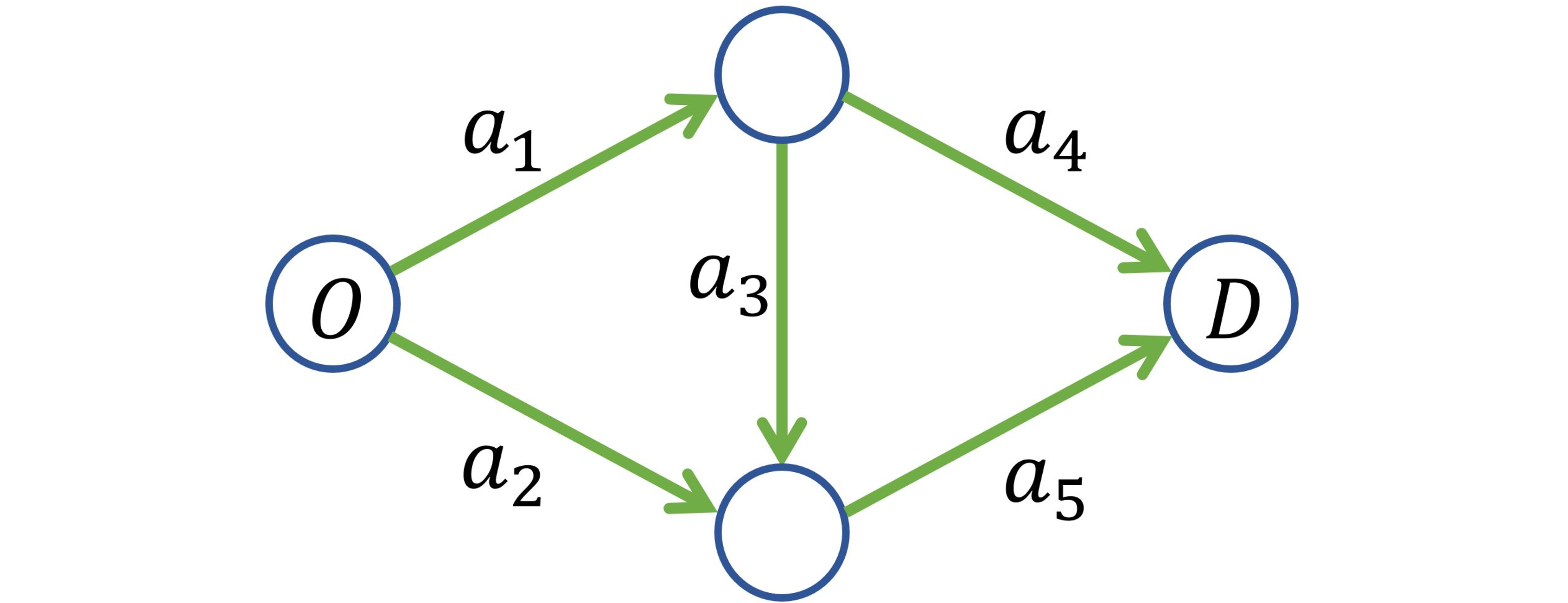
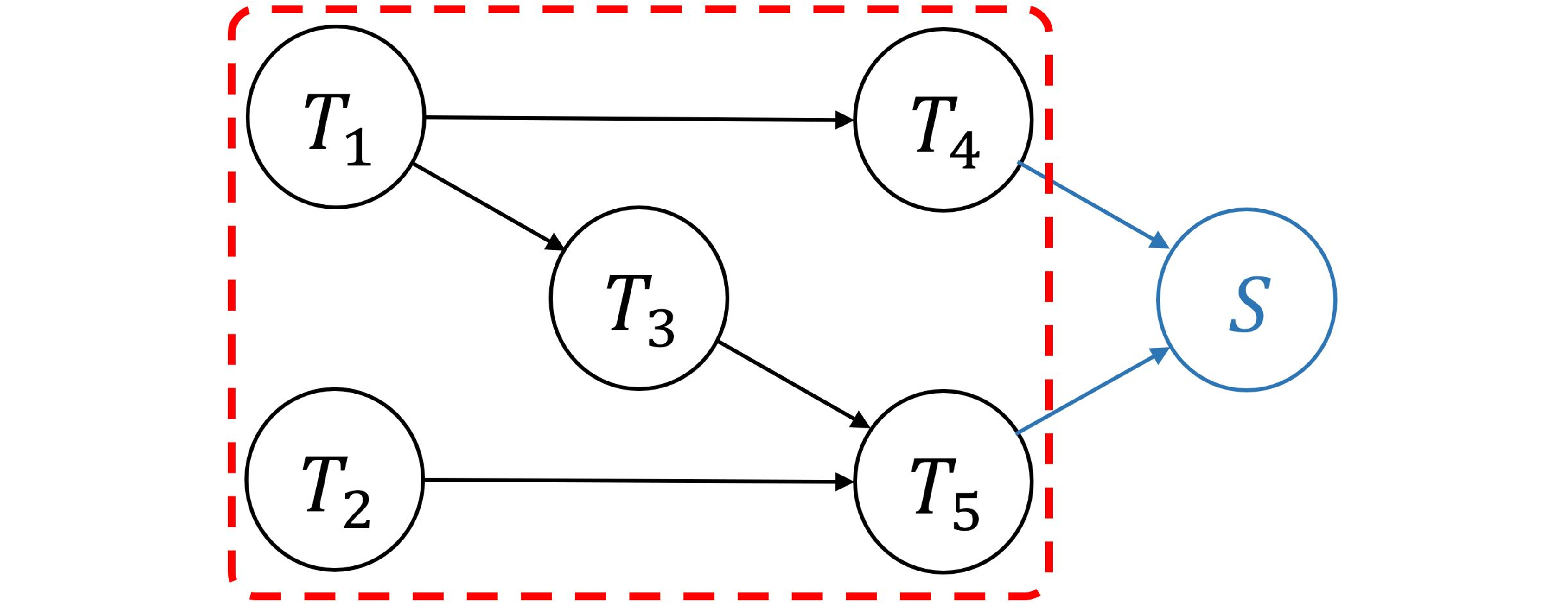
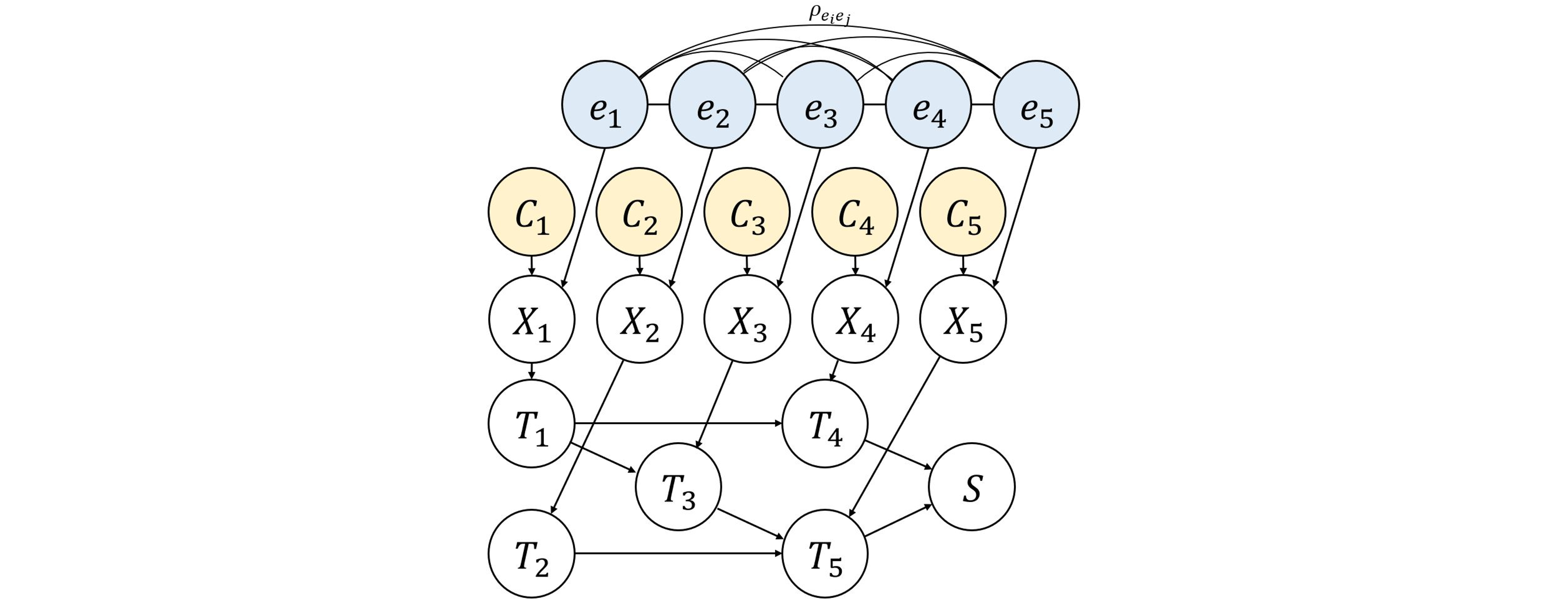
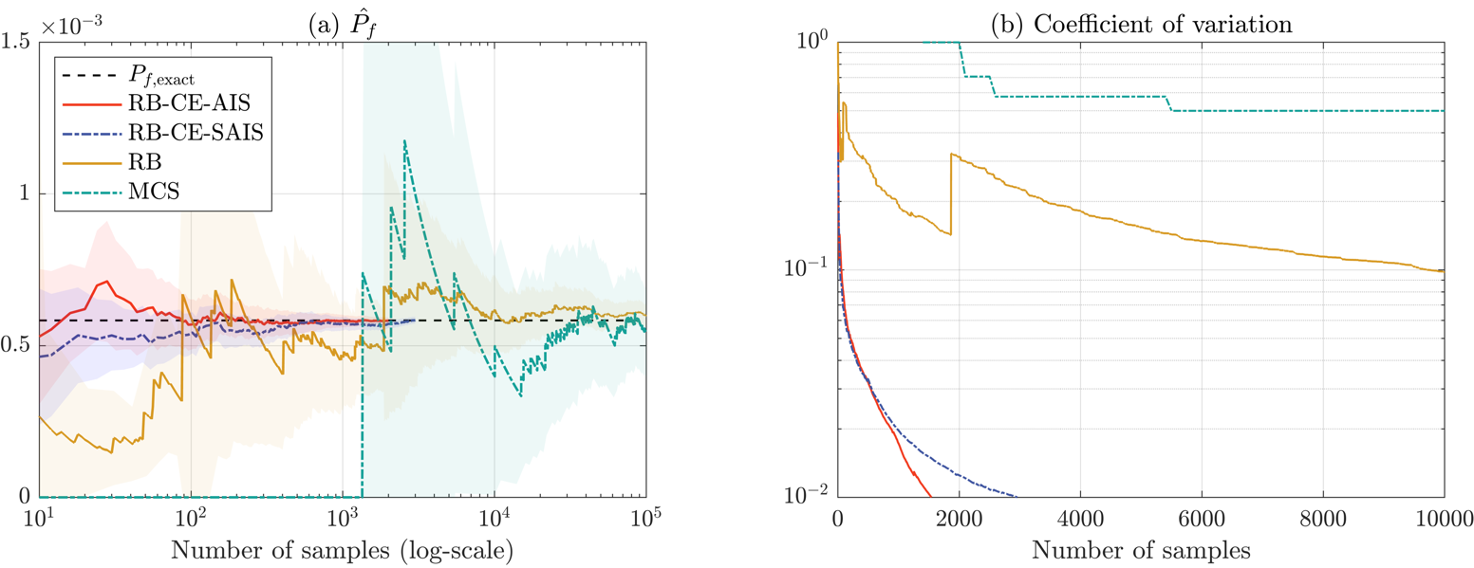
This paper proposes a novel Bayesian network (BN)-based method for system reliability analysis (SRA), which employs the junction tree algorithm and dual graphs. The proposed integration of graph theory and BN approach enables a systematic automation of BN modeling for SRA, thereby evaluating the sys-tem failure probability and parameter sensitivity analytically especially when component events are statistically independent. Furthermore, a new metric for complexity quantification in terms of the required memory is proposed. To extend these proposed methods to seismic SRA with dependent component events, we also propose incorporating importance sampling and Rao-Blackwellization into the proposed method.
Abstract
Modern societies depend on various lifeline networks such as transportation, electricity, and gas distribution systems, which are vulnerable to seismic events. Although numerous analytical and simulation-based methods have been developed for efficient seismic system reliability analysis (SRA), dealing with high-dimensional events arising from large-scale infrastructure networks remains challenging. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a system reliability method that efficiently computes the connectivity of directed graphs. The method employs the dual graph representation of a target system to automate the construction of a Bayesian network (BN). This enables the application of the junction tree algorithm, a well-established BN inference method, to perform reliability analysis and quantify complexity based on a network topology. The paper further tackles SRA challenges associated with fully correlated seismic uncertainties, which typically lead to a significant increase in computational complexity. To this end, we propose to combine a cross entropy-based adaptive importance sampling technique with Rao-Blackwellization. Thereby, sampling methods and exact analytical inference can be effectively combined to improve computational efficiency for seismic SRA of lifeline networks. The proposed methods are demonstrated through three numerical examples.
Acknowledgment
- This work is supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (RS-2021-NR059025). The first author is also supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the NRF funded by the Ministry of Education (RS-2024-00408907). The third author is also supported by the Institute of Construction and Environmental Engineering at Seoul National University.
References
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: